Vulnerable digital platforms put millions of users’ data at risk everday. A data breach can occur on any system or application, from top-tier social media platforms to small IT service provider apps. Most of the time data breaches occur due to poor system set up often due to a lack of cyber security skills.
Not all breaches are the same. Some are caused by a faulty system or bugs in the software or inexperienced programmers. As more and more companies build their online presence, a significant part of their business is online-based and therefore vulnerable. A business may only have a few products or services showcased and a simple payment option on their website but that is enough for hackers to cause some real damage and for significant data breaches to occur.
Let’s go through some notable breaches:

Facebook API bug: Even though API makes interaction with web functionality easy, it can put information into the wrong hands if not handled correctly. In 2018 a photo API bug on Facebook enabled third-party apps to see pictures belonging to nearly 7 million users the apps weren’t authorized to access. This may have allowed up to 1,500 apps from 876 developers to inappropriately access people’s pictures. The bug also allowed some third-party apps to see photos that people had uploaded to the Facebook platform but hadn’t shared.

Log4j vulnerability: java-based Log4j is a widely used functionality for web programs. As used in most services, the Log4j vulnerability exposed hundreds of industries to potential attacks. Even tech giants such as Amazon, Google, Twitter, and Microsoft suffered from exposure. Nearly one-third of the world’s web servers use java, and Log4j is a critical functionality. Over 3.7 million hacking attempts with 46 per cent of familiar malicious entities are recorded.

Colonial Pipeline ransomware cyber attack: On May 7, 2021, Colonial Pipeline, an American oil pipeline system that carries gasoline and jet fuel mainly to the Southeastern United States, suffered a ransomware cyberattack that impacted computerized equipment managing the pipeline. The company was forced to stop all pipeline operations to contain the attack and had to pay $4.4 million to the hacker group calling themselves DarkSide. It was the largest cyberattack on an oil infrastructure target in the history of the United States. Darkside is believed to have stolen 100 gigabytes of data from company servers the day before the malware attack.
Prevention Role
It doesn’t matter how secure a system is, it is always vulnerable to hackers. According to statistics, almost two-thirds of businesses have lost revenue due to security issues, most of which occurred due to errors made by unskilled developers. IT skills and cybersecurity skills are not the same thing. Often startups and new businesses want to tackle both in the same budget. Cybersecurity professionals can be found within the IT department but they have to be top-notch. For this reason, many companies work with managed services providers (MSPs) to provide a simpler solution and access the security skills needed.
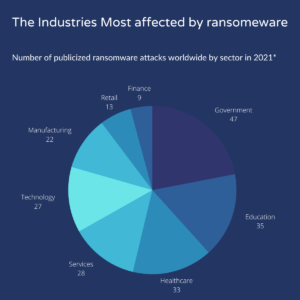
Sixty-four percent of organisations lost revenue in 2021 due to ransomware attacks. It is not a new phenomenon, but the post-pandemic use case for ransomware attacks grew tenfold. For C-level executives, the cybersecurity skill gap is a crucial concern. Sixty percent of leaders struggle to find the right candidate to tackle advanced cyber threats. Fifty-two percent of C-level executives reported that it is challenging to retain talent.
Organisations are looking to hire diverse teams to handle critical situations rather than training them to a certain level, which may take a while. “Zero-day” software vulnerability is another intriguing concept. It is an excellent opportunity for seasoned veterans to find loopholes in company software. Without a proper skillset, this vulnerability may remain unexposed and undetected.

